Social benefits
Germany is a welfare state. What does this mean? Basically, all citizens should take care of their own livelihoods. However, people who are not or only partially able to make sure that they can provide for themselves, are being helped by the state. The state will compensate disadvantages and in order to do so, there are a number of social benefits.
Listed below, you will find the most important social benefits in an overview:
Provisions under the asylum seekers benefits act (Asylb(LG)
Tolerated applicants for asylum and foreigners who have the right to stay in Germany as they have submitted the application for asylum, are entitled to receive benefits according to the asylum seekers benefits act.
The benefits included are:
- basic benefits for food, housing, heating, clothes, healthcare, household, consumer goods and consumables (necessary needs)
- benefits intended for personal needs of daily life (necessary personal needs)
- benefits when being ill, pregnant and given birth
In case special circumstances are applicable, additional benefits may be granted. Detailed information can be obtained at your competent social centre.
Adresses:
Education and participation (educational package)
Recipients of benefits accordingly to the Asylum seekers benefit act, can in addition submit an application for their children, concerning benefits for education and participation.
You can find general information about the educational package under the menu item all information from A-Z under education and participation, as well as the application on the website from the county https://www.schleswig-flensburg.de/?fdirect=1
Benefits according to the SGB II (unemployment benefits II, colloquially Hartz IV)
Benefits according to the SGB II can be applied for if:
- the applicant is at least 15 years old and has not reached a certain age limit
- Is fit for work (can at least work for 3 hours per day)
- Is in need of help (cannot support the own livelihood)
- The normal place of residence is within Germany
The basic idea from the SGBII is called: supporting and fostering. Unemployed are encouraged to search for a work or vocational training. Mainly it is the aim to find employment which generates and safeguards enough income (Money) for a single person respectively the whole family. How this aim is reached, is determined (in a joined contract) in an integration agreement.
By means of diverse offers, clients are specifically fostered (financial support)
The following benefits can be applied for:
- Benefits that safeguard the livelihood (basic needs, additional needs, costs of housing and heating, premiums for health and nursing care insurance)
- Benefits that enable work integration
- Benefits for education and participation
The application for SGB II has to be filled at the respective social centre. For addresses, please check the menu item, AsylbLG.
Education and participation (educational package)
Recipients of benefits accordingly to the Asylum seekers benefit act, can in addition submit an application for their children, concerning benefits for education and participation.
You can find general information about the educational package under the menu item all information from A-Z under education and participation, as well as the application on the website from the county https://www.schleswig-flensburg.de/?fdirect=1
Benefits for families with children
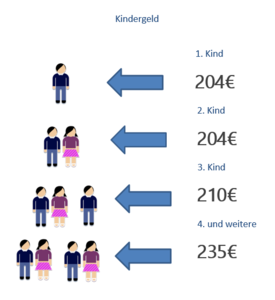
Child benefits
Legal guardians and parents can apply for child benefits
Child benefits are provided:
- For children who are in vocational training until the age of 25
- For unemployed children until the age of 21
- For children who live in Germany or in a member state of the EU or the EWR
The child benefits are paid independent from the income.
In addition, families can be granted child allowances for the income tax.
On the 1st of July 2019 (1.7.2019) the child benefits were raised once again and is currently
The application happens via the Familienkasse der Agentur for Arbeit.
Child supplement
Child supplement can be paid to families with a low income if:
- unmarried children below the age of 25 and are living in the same household
- the income is not below a certain minimum threshold. This minimum threshold is at € 900 gross for couples and at €600 gross for single parents
- the applicant does not get any benefits according to SGB II or welfare.
From the 1st of January 2020, you can get the child supplement as well, if your total income is less than €100 underneath the entitlement to SGB II. This total income consists out of your income, child supplement and housing benefits.
The current valid maximum income threshold has been cancelled since the 1st of January 2020. This enables you to get the child supplement, even if you have a slightly higher income.
The maximum amount of the child supplement is €185 per child and month.
You can get the application at the family cashier, but also you can download it online.
In addition, parents may apply for educational and participatory benefits. Please refer to education and participation under the menu item Overview from A to Z.
Parental benefits
Parents will get the parental benefit, if they:
- supervise their children for a maximum time period of 14 months after they were born
- do not work more than 30 hours during their parental leave
- live together with their child in one household
- have a residence or their usual centre of living in Germany
Besides the basic parental benefit (parental benefit) there is since 2015 the parental benefit plus available.
Basic parental benefit
If both parents are not able to work because of the necessity to supervise their child, then the basic parental benefit is granted for the duration of 14 months for both. These months can be divided between both parents freely. One of the parents can make use of the benefit for at least 2 months and for a maximum of 12.
Single parents who get the parental benefit can make use of the parental benefit for the full 14 months. Parents can only get the basic parental benefit within the first 14 months of life of their child. After that, they can only get a parental benefit plus or the partner bonus.
Parental beneift plus
The parental benefit plus aims to facilitate the compatibility of occupation and family for parents who want to work part-time again, for as long as they get the regular parental benefits. Mums and dads have therefore the possibility, longer than before, to take advantage of the regular parental benefit.
Parental benefit plus can be received twice as long as the regular parental benefit: One month parental benefit equals two months parental benefit plus.
If parents do not work after their child was born, then the parental benefit plus is only half as high as the monthly parental benefit including part-time.
Partnership bonus
Parents get a partnership bonus, who share the supervision of their child while receiving the parental benefit and at the same time work in part-time between 25 and 30 hours per month: They get four extra months of parental benefit plus. Single parents are entitled to the total partnership bonus.
All parents are entitled to parental benefit, no matter if they were working before the birth of their child or not. The amount of the parental benefit is dependent on the income.
Parents with a higher income get 65%, and parents with a lower income up to 100% from their prior income.
Depending on the income, the parental benefit is between €300 and €1800 per month. The parental benefit plus is between €150 and €900 per month.
All parents who, after the child was born, supervise it them-self and work a maximum of 30 hours per week, receive the minimal parental benefit. Also those are concerned who were not able to work because of the supervision of older children, such as students, housewives, housemen and parents.
With an online calculator for parental benefit you can determine the amount of the parental benefit yourself. You can use this link for the online calculator. LINK
The parental benefit has to be applied for in written form. Please contact your competent office for parental benefits.
Adress:
Maternity benefit
the entitlement for a maternity benefit concerns women who:
- are voluntary or are statutory health ensured and have an entitlement to get sick pay
- were employed (home-based work or mini-job) before the child was born
- were admissibly given notice to by their employer while being pregnant
During the period of protection, maternity benefit is paid (the women are not allowed to work during this time) for the duration of:
• 6 weeks prior to giving birth and 8 weeks after
• 12 weeks after giving birth in case of a premature- or multiple birth
As how much the maternity benefit is, will be calculated upon the income from the last three months and is a maximum of €13 per day.
In case, the income prior to maternity leave was more than €390, an employer contribution will be paid in addition to the maternity benefit.
You will find additional information to the topics: family, pregnancy, women, on the website from the Federal Ministry of Family, Seniors, Women and Youths.
Guideline to the maternity protection
Housing benefit
Housing benefit (rent subsidy ,or as an owner, a subsidy to the costs) may be applied for by families with a low income.
The amount of the housing benefit is calculated based upon:
- the income and number of family members
- how much is the actual rent or the costs are
Additional information as well as the application can be found on the website of the county. LINK
People who are entitled to housing benefit may additionally file an application for educational and participatory benefits for their children. Check education and participation under the menu item, all infos from A-Z.
Unemployment benefit I (in casee of job loss)
Unemployment benefit can be applied of employees who are currently without a job.
Seen as unemployed is an employee if he or she
- Is not within an employment
- tries to end his or her unemployment
- Is available for the job market (the facilitation efforts of the Federal Labour Agency)
Unemployed must report personally at the Federal Labour Agency and must have been socially statutory insured in order to have the entitlement.
After fulfilling the conditions, the unemployment benefit will be paid between 6 and 12 months. For older unemployed, the unemployment benefit may be granted for as long as 24 months.
Unemployed have to try to get a social statutory ensured employment (at least 15 hours). There will be counselled by the Federal Labour Agency regularly.
You can get further information on the website of the Federal Labour Office.
Educational Grant (BAföG)
The Federal Education and Trainings Assistance Act regulates the federal assistance of the vocations of pupils and students. For one thing, the vocational subsidy is meant to enable equally of chances, and on the other hand give socially weaker citizens a chance to get a vocational qualification.
Educational support is granted for apprentices who generally at the start of the vocational training are not older than 30 years old. However, there are exceptions to this rule. For example, apprentices who because of family reasons were not able to begin the vocation. Additional exemptions are made for students. Further information is available here.
According to the educational grant (BAföG), the attendance of the following schools and institutions can be promoted:
- mainstream schools from the 10th grade (Pupil BAföG)
- vocational schools (Pupil BAföG)
- specialised secondary classes (Pupil BAföG)
- evening secondary school, vocational school, evening middle school, evening high school and colleges (Pupil BAföG)
- academies and Universities (study BAföG or study loan)
- new: private vocational academies (study BAföG or study loan)
Apprenticeships within the dual system cannot be promoted according the BAföG. Training support grant (BAB) can be applied for under certain conditions.
The amount of the grant depends on the type of the training facility and housing.
With an online calculator you can determine the amount of the grant by yourself. You can use this link for the online calculator.
BAföG is not only available for German citizens but also for citizens coming from the European union, migrants and refugees, who live in Germany. BAföG can be granted as a financial aid during studying or schooling. A basic rule is: If foreigners have a good perspective of staying in Germany and are socially integrated, they are seen as being eligible for aid.
The receiving of BAföG depends on the residency status of a refugee.
Accepted refugees (accepted and entitled for asylum, refugees whose status has been approved, respectively refugees who have subsidiary protection) can, no matter how long they already are in Germany, apply for BAföG.
Tolerated migrants and holders of certain humanitarian resident permits are also entitled if they are already in Germany for 15 months (compare §8 BAföG, section 2.2 and section 2a).
General information concerning the topic BAföG can be found on the website from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research
Down below you can find overviews concerning the access for educational promotion of refugees, citizens from the EU and from non-member countries, put together by the specialist unit Immigration of the promotional program „Integration by qualification (IQ)“.
- PDF-Datei: (PDF, 1 MB)
- PDF-Datei: (PDF, 688 kB)
- PDF-Datei: (PDF, 396 kB)
Vocational training grant (BAB)
Apprentices can apply for a vocational training grant if they do not live with their parents and fulfil certain conditions ( Apprentices-Azubis). The grant can also be given to participants who are within a vocational preparation course (BvB).
The vocational training grant is a sponsorship from the Federal Labour Office. The amount of the BAB depends, during the vocational training on:
- the type of housing
- the amount of the salary earned by the apprentice
- the annual income of the parents, the spouse or the companion
The sponsorship has a flat-rate for the livelihood and covers costs that are related to the vocational training, for example travel costs and costs for work clothes.
BAB can also cover external vocational training (not within a company).
Apprentices, who have their own household and are receiving the BAB, can get a subsidy according to social security statute book, second book, basic covering for job seekers (SGB II).
Condition to get the subsidy is, that the BAB plus any other income does not cover the costs for housing and heating. Unreasonable high costs cannot be taken into account.
The vocational preparation education programme (BvB) covers training course costs, necessary travel costs, costs for training material and work clothing, independently from the income but partially according to flat-rate contributions. Special regulations apply for apprentices with disabilities in order to support them to be able to participate in professional life.
For tolerated people and people who are permitted to stay in Germany for the asylum proceedings.
For the first 15 months that you live in Germany and receive social benefits according to §3 AsybLG, they may be continuously be paid, even if you begin a vocational training and do not receive a vocational training grant.
Tolerated people who have access to the labour market are entitled to receive, after 15 months, the vocational training grant.
Further information can be found on the website of the Federal Labour Agency.
Benefits according to SGB XII
Social welfare includes help for livelihood, the basic covering when having become elderly and when suffering from reduction in earning capacity as well as benefits in special living situations, for example the need for care.
Entitled to social care benefits only exists, if the need can’t be covered by own means.
The aid to support the livelihood can be received by people who are not able to work and already get a temporary full-rate reduced-earning-capacity pension, are long-term sick or are taken care of in an institution.
Entitled to a basic covering are people needing help, aged 65 and more, people suffering from reduction in earning capacity, as well as people aged 18 and more, who are permanently not able to work because of medical reasons and are fully reduced in their earning capacity (People, who permanently are not able to work more than 3 hours per day).
You can find further information on the website of the county (LINK) under the menu item, social issues.
Education and participation (educational package)
Recipients of benefits according to SGB XII can apply for educational and participatory benefits on behalf of their children.
You can find general information concerning the educational package under the menu item overview from A-Z under education and participation. You can find the application form on the county website https://www.schleswig-flensburg.de/?fdirect=1
Retirement pension
The statutory pension is payed the moment the insured person has reached a certain age (statutory retirement age) and was at least statutory ensured for 5 years (general waiting period).
Insured, who were born before the 1st of January 1947, can retire when they have completed their 65th year of life. For later age groups, the general statutory retirement age will be steadily increased step by step between 2012-2029, from age 65 to 67.
The amount of the retirement pension depends on how long the statutory insured employment was lasting, as well as how high the achieved monthly income was.
There are also different forms of retirement pensions.
Additional information can be found here